Immunoglobulins
Online Biology Dictionary
|
|
|
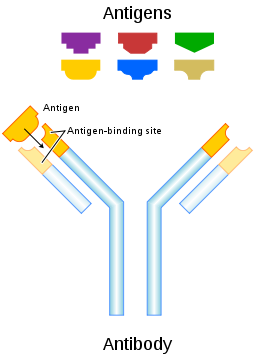
Immunoglobulins (/im-MYOON-ə-GLAWB-yə-linz/), or antibodies (/AN-tə-BAWD-eez/), are secreted by plasma cells in response to antigens.
Each antibody couples specifically with its antigen (and with molecules that are chemically very similar to its antigen). Antibodies are Y-shaped, tetrameric molecules made up of two long polypeptide chains, the heavy (H) chains, and two short chains, the light (L) chains. Each arm of the Y-shaped structure binds a specific antigen and each plasma cell produces one and only one type of antibody. There are five groups of heavy chains (alpha, delta, epsilon, gamma, and mu), which are used in naming the five specific classes of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM respectively).
Immunoglobulins in detail:
Most shared on Macroevolution.net:
Human Origins: Are we hybrids?
On the Origins of New Forms of Life
Mammalian Hybrids
Cat-rabbit Hybrids: Fact or fiction?
Famous Biologists
Dog-cow Hybrids
Georges Cuvier: A Biography
Prothero: A Rebuttal
Branches of Biology
Dog-fox Hybrids