Leukocytes
Online Biology Dictionary
|
|
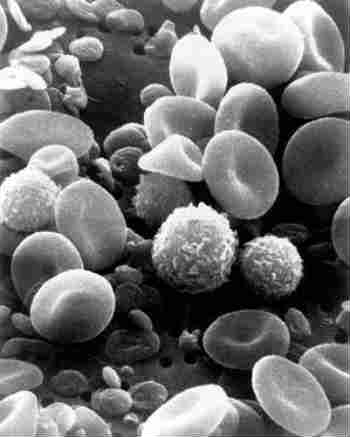 Cellular constituents of normal blood. Leukocytes can be seen as fuzzy, irregularly-shaped cells. Also visible: disk-shaped erythrocytes, and tiny, flat platelets.
Cellular constituents of normal blood. Leukocytes can be seen as fuzzy, irregularly-shaped cells. Also visible: disk-shaped erythrocytes, and tiny, flat platelets.
Leukocytes (also leucocytes, white cells, white blood cells, or white blood corpuscles) are cells of the immune system that rid the body of debris and protect it against contagious disease. They arise from the same cells (hematopoietic stem cells), residing in the bone marrow, that can alternatively mature into erythrocytes. They are able to enter tissue and return to the blood stream.
Normally there are between 4×10⁹ and 1×10¹⁰ white cells in a liter of human blood. Leukocytosis, or leukopenia, is the name given to the condition where white cells are present at an elevated level, which is a frequent occurrence in disease.
Pus is composed of dead white cells that have been overcome by bacteria. The term "white blood corpuscle" is derived from the fact that these cells show up in centrifugated blood as a white layer.
There are several types of white cells:
as well as the
- polymorphonuclear
- granulocytes: neutrophils,
- eosinophils, and
- basophils.
Most shared on Macroevolution.net:
Human Origins: Are we hybrids?
On the Origins of New Forms of Life
Mammalian Hybrids
Cat-rabbit Hybrids: Fact or fiction?
Famous Biologists
Dog-cow Hybrids
Georges Cuvier: A Biography
Prothero: A Rebuttal
Branches of Biology
Dog-fox Hybrids