Telomeres
Online Biology Dictionary
Video: Effects of telomeres on health and longevity.
|
|
EUGENE M. MCCARTHY, PHD GENETICS
|
|
| The 46 human chromosomes are shown in blue, with the telomeres appearing as white dots. The DNA has already been copied, so each chromosome contains two identical, strands of DNA, each capped by a telomere at both ends. |
Telomeres are DNA sequences composed of simple repeats at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes (see figure right). They stabilize linear chromosomes by protecting their ends from loss during replication (prokaryotic chromosomes are circular).
During interphase, the enzymes that duplicate the chromosomes cannot continue replication all the way to the chromosomes' ends. Instead, a single stranded template for each telomere is built by the enzyme telomerase reverse transcriptase, abbeviated TERT, or in humans hTERT (see diagram of TERT's function below). This template is then used by DNA polymerase to complete synthesis of the new telomere.
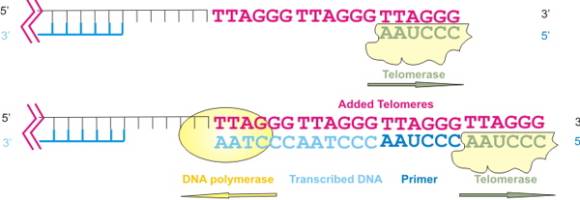
|
|
A telomere is constructed by means of a two-step process: (1) telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) synthesizes a template strand; and (2), DNA polymerase synthesizes a second strand on the template. |
Most shared on Macroevolution.net:
Human Origins: Are we hybrids?
On the Origins of New Forms of Life
Mammalian Hybrids
Cat-rabbit Hybrids: Fact or fiction?
Famous Biologists
Dog-cow Hybrids
Prothero: A Rebuttal
Branches of Biology
Dog-fox Hybrids